

Written by Stephen Day
Gas Safe Engineer
Updated: 6th February, 2026
Here at iHeat we’re boiler experts, this includes an extensive bank of component knowledge, and we aim to help educate and inform our customers in any way we can.
Get a new boiler quote, save up to £550 per year (0% APR available).
In this blog we’re going to be exploring boiler circulation pumps in particular, including their function, common issue troubleshooting and price guidance for component replacement.
A boiler circulation pump does exactly what it says on the tin, boosts the movement of water within a heating system to better enhance its function.
A circulation pump is often located within the boiler or in some cases in an airing cupboard next to the hot water cylinder.
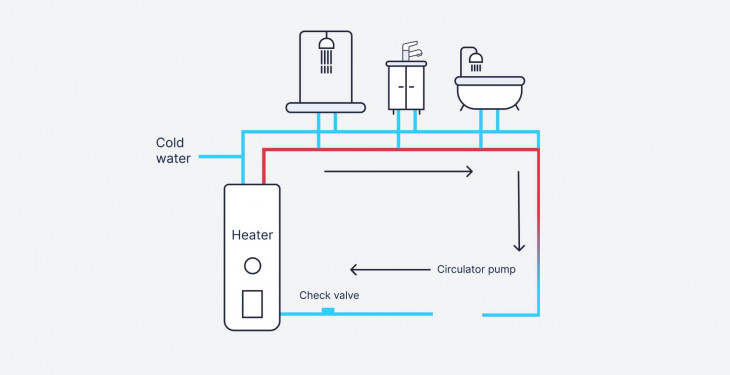
The water travels from your boiler through to the pipes that feed your radiators, towel rails and hot water cylinder, the water then flows back through the boiler to maintain a constant circulation of heated water around the property.
As a crucial component within the transitory functionality of a central heating system, any damage to this component can lead to the owner having a decreased performance from their boiler, wasting energy and subsequently money.
A water leak emanating from the pump
The pump is making an unusual noise
The water flow pipe isn’t hot despite the pump being operational
You have no hot running water
Some (or all) of your radiators aren’t heating up
Incorrect speed settings
Incorrect installation
Leaking pump
Pump won’t switch off
Loss of power
No water running through system
Although in some cases it can be convenient to attempt minor boiler repairs yourself, it’s always prudent to arrange any repair, servicing or maintenance of your boiler to be carried out by a Gas Safe registered engineer. This is a fully trained and qualified gas engineer who is legally licensed under the published Gas Safety (Installation and Use) Regulations 1998 (GSIUR).
The Gas Safe Register is the appointed representative of the safety regulatory group- Health and Safety Executive.
All registered Gas Safe engineers should carry and be able to present official accreditation and have a verified and unique ID number.
All of our iHeat engineers are registered Gas Safe!

As with any type of boiler component replacement, there are a few factors that may influence the eventual total for the new part and labour costs.
The boiler brand, boiler style and model, merchant rates and engineer labour rates will all directly affect the amount you will be required to pay in order to fix a faulty or broken circulation pump.
You can expect to pay around £150-£300 (including installation fees) for a top quality circulation pump, with the pump price itself usually ranging from £95-£150 and professional labour costs usually in the region of £100-£150.
Grundfos is a renowned and celebrated water pump manufacturer, and many of their domestic pumps offer a premium choice when it comes to providing a strong supply of circulating water throughout a property.
Some high quality domestic Grundfos pump models include-
UPS2 15-60
UPS2 25-80
Alpha 2 L 15-50
Alpha 2 L 15-60
While an individual component such as a circulation pump can be replaced in isolation, if your boiler is starting to show signs of more serious or repeat decay, it may be beneficial to upgrade to a newer, more efficient boiler.
The best way of ensuring your boiler is operating as it should, is by proactively replacing ageing or faulty boilers at the earliest signs of degradation, this preventative step is far more prudent than reactive maintenance.
It’s a mechanical and engineering fact that due to some of the technological advancements in recent times, modern boilers are more robust and efficient than anything made previously.
Last updated: 6th February, 2026

Written by Stephen Day
Gas Safe Engineer at iHeat
Stephen Day is a Gas Safe registered and FGAS certified engineer with over 20 years of hands-on experience in the heating, cooling, and renewable energy industry, specialising in boiler installations, air conditioning, and heat pump systems.
LinkedInArticles by Stephen Day are reviewed by iHeat’s technical team to ensure accuracy and reliability.

19th February, 2026
Selecting the appropriate boiler for your London home involves understanding the different...
 Read Article
Read Article

19th February, 2026
A typical Annual Boiler Service includes a visual inspection to identify any obvious fault...
 Read Article
Read Article

19th February, 2026
Boiler servicing comprises a set of inspections and tests conducted by a qualified enginee...
 Read Article
Read Article
No obligation. Takes less than 60 seconds.