

Written by Stephen Day
Gas Safe Engineer
Updated: 22nd September, 2025
This blog comprehensively compares heat pumps and gas boilers, focusing on their efficiency, technology, costs, and performance in different climates. Equip yourself with valuable insights to make an informed and energy-efficient decision for your home heating system.
Get a new boiler quote, save up to £550 per year (0% APR available).
The debate between heat pumps and gas boilers has been gaining attention as homeowners and businesses seek more energy-efficient and environmentally-friendly heating options.
Heat pumps are devices that extract heat from the outside air and transfer it inside a building, providing warmth during colder months.
On the other hand, gas boilers rely on the combustion of natural gas to produce heat, which is then distributed through radiators or underfloor heating systems.
Get a quote in 60 seconds, fitted as fast as next day!
0% APR finance available.
As technology advances, it becomes essential to understand the differences in efficiency and determine the best choice for heating systems.
Efficiency is a crucial factor when comparing heat pumps to gas boilers. In general, heat pumps are considered more energy-efficient as they use electricity, which can be generated from renewable sources, to transfer heat from the environment.
Gas boilers, however, burn fossil fuels like natural gas, which are non-renewable and contribute to greenhouse gas emissions.
Performance in different regions may vary, with heat pump efficiency decreasing in very cold climates while gas boilers may remain constant.
Find out more about heat pumps in our 2025 cost guide!
Heat pumps and gas boilers are two primary options for a home heating system. Each has its benefits and drawbacks, but when it comes to efficiency, heat pumps have the edge in certain situations.
Heat pumps extract heat from the outside air and transfer it inside your home, providing warmth in the winter months.
This process relies on electricity, which can come from renewable sources. On the other hand, gas boilers use natural gas—a fossil fuel and non-renewable resource—to heat the home and hot water supply.
In terms of efficiency, a heat pump can transfer up to 300% more energy than it consumes.
This makes it more energy-efficient than gas boilers in moderate climates, where the outdoor temperature remains within the heat pump's rated range.
However, when outdoor temperatures drop significantly, the efficiency of a heat pump may decrease, making a gas furnace a better option in areas with freezing temperatures.
Gas furnaces come in different efficiency levels, with standard variants operating at around 80% efficiency and high-efficiency models reaching up to 95%.
Although natural gas is often less expensive than electricity, higher fuel costs may offset the cost advantage of a gas furnace.
Contrary to popular belief, gas furnaces are not always more efficient than heat pumps. In fact, heat pumps can be more economical, despite their higher installation costs, especially in areas with milder winters.
Ensuring that a heat pump operates at optimal efficiency requires regular maintenance, including the cleaning of filters and coils, as well as periodic inspections and servicing.
When considering space-saving options, both heat pumps and gas boilers offer similar compact designs. A gas boiler is typically located in a cupboard, utility room, or loft, while an air source heat pump's primary unit is installed outdoors, leaving more indoor space available.
To summarise, heat pumps and gas boilers differ in their fuel sources, operating principles, and efficiency rates. Heat pumps are generally more energy-efficient in milder climates but may lose efficiency in extremely cold conditions.
Gas boilers offer an alternative heating option, with varying efficiency levels depending on the specific model and type. With this information in hand, homeowners can make informed decisions about the best heating system for their needs.
Heat pumps and gas boilers both serve as heating systems, but their efficiency levels and energy usage can differ significantly. To better understand their efficiency, let's explore the factors contributing to each system's performance, considering energy efficiency, heating costs, and flow temperature.
Heat pumps are known for their high energy efficiency. They operate by extracting heat from the outside air and transferring it inside your home. This process uses a fraction of the energy, making heat pumps particularly suitable for moderate climates.
As the temperature drops, however, their efficiency can decrease, leading to higher energy bills.
In contrast, gas boilers produce rapid heat, making them more suitable for older, less efficient buildings. Although natural gas is generally cheaper than electricity, gas boilers aren't always more efficient than heat pumps. In fact, in very cold climates, a gas furnace might be slightly more efficient due to the lower heating costs associated with burning natural gas.
When examining flow temperature, heat pumps work well with lower temperature systems such as underfloor heating, as they can deliver warmth consistently over a larger surface area.
Gas boilers, while capable of adapting to work with low-temperature systems similar to heat pumps, generally excel at producing high-temperature heat more effectively.
In summary, heat pumps tend to be more energy-efficient in moderate climates where the temperature does not fall too low, leading to lower energy bills.
Gas boilers, on the other hand, offer advantages in colder regions and older buildings by providing quick, high-temperature outputs. Ultimately, the efficiency of a heating system relies on the region, building conditions, and individual user preferences.
Heat pumps offer substantial benefits over gas boilers when it comes to energy efficiency and environmental footprint. With an energy efficiency rating that's 3 to 5 times higher than natural gas boilers, heat pumps present a greener alternative for home heating.
They offer protection against the fluctuating costs of fossil fuels and contribute to a significant reduction in carbon dioxide emissions.
When paired with renewable energy sources, electric heat pumps significantly lower CO2 emissions compared to gas condensing boilers. Adopting heat pumps globally over traditional boilers could decrease carbon emissions by an impressive 3 gigatons annually.
As the electricity grid continues to decarbonise, the emissions from heat pumps will further decline, making them a superior choice to natural gas boilers in all areas before 2025.
Heating for homes and businesses is a major contributor to greenhouse gas emissions, thereby playing a role in climate change.
By opting for heat pumps over natural gas boilers, homeowners can play their part in reducing their carbon footprint, which is critical for meeting global climate objectives.
Government policies to increase the market penetration of heat pumps can help accelerate the decarbonization process.
In conclusion, heat pumps, with their higher energy efficiency and lower environmental impact, offer a promising alternative to gas boilers.
By decreasing carbon dioxide emissions, this innovative technology helps mitigate climate change and encourages the use of renewable energy in residential heating systems.
When considering the efficiency of heat pumps compared to gas boilers, it's essential to examine the financial aspects involved. Cost factors encompass initial investment, installation, maintenance and repair, as well as potential incentives and rebates.
The cost of installing a heat pump typically ranges from £1,800 to £20,000, with an average expenditure of around £4,000.
However, this can jump up to £40,700 if the project demands a more complex solution, such as a geothermal heat pump system. On the other hand, a gas boiler installation can run between £1,500 and £4,000, depending on the type and brand of the boiler.
Heat pumps are known for their energy efficiency, which often results in lower utility bills. While upfront installation costs for heat pumps may be higher than gas boilers, the long-term operational costs are generally lower.
Additionally, heat pumps require minimal maintenance, which translates to reduced repair costs. Gas boilers, on the other hand, need annual service checks and can incur higher maintenance and repair expenses.
In terms of financial incentives, various rebates and grants are available to promote the use of heat pumps. These incentives contribute to lowering the overall cost of the system. It's worth noting that gas boilers might not be eligible for similar incentives due to their higher carbon emissions.
Investment in a heat pump can yield a better return on investment in the long run, thanks to lower energy consumption and utility savings.
However, this largely depends on the local energy prices and climate conditions. In colder regions where natural gas is abundant and cheaper, a gas furnace might prove to be a more cost-effective option.
It's clear that the choice between a heat pump and a gas boiler involves more than just comparing upfront costs. While heat pumps generally offer greater energy efficiency and lower operational expenses, factors such as local energy prices and climate must also be considered.
Thus, weighing the long-term financial implications of each system is crucial for making an informed decision.
When considering the efficiency of heat pumps and gas boilers, it is essential to examine their performance in various regions. Numerous factors, including temperature, climates, and location, can significantly impact the performance of these systems.
In colder climates, such as the Northeast, heat pumps may not perform as well as gas boilers. As the outside temperature decreases, the efficiency of heat pumps also tends to decline.
However, advancements in technology have led to the development of cold-climate heat pumps, which can provide consistent heating in temperatures as low as -25°C.
While these models are more efficient than older heat pump systems, they may still not be as efficient as gas boilers in extremely cold regions.
In contrast, heat pumps perform better in milder climates where the difference between indoor and outdoor temperatures is minimal.
This allows heat pumps to take better advantage of the ambient air's heat, yielding better efficiency.
Gas boilers, on the other hand, may not achieve their full efficiency potential in milder climates, as they rely on burning fossil fuels which can be costlier and produce higher emissions compared to electricity-powered heat pumps.
Region-specific energy prices also play a role in determining the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of heat pumps versus gas boilers. In some regions, the cost of natural gas is lower than that of electricity, which may make gas boilers a more cost-effective choice.
On the other hand, other regions might have higher gas prices or policies promoting renewable energies, making heat pumps a better option.
To summarise, the performance of heat pumps and gas boilers varies across different regions, with factors such as temperature, climate, and energy prices affecting their efficiency.
In colder climates, gas boilers may be more efficient, while heat pumps are likely to excel in milder climates. Ultimately, the choice between these systems will depend on local factors, including energy prices and environmental policies.
Air source heat pumps (ASHPs) use ambient air to heat or cool your home. These systems extract heat from the air during winter and use the same principle to cool your home in summer.
They are a popular choice due to their ease of installation and lower initial cost compared to other heat pump types. ASHPs are typically installed outdoors and can be air-to-air, which uses a ducted system to distribute heat, or air-to-water, which utilises underfloor heating or specially designed radiators.
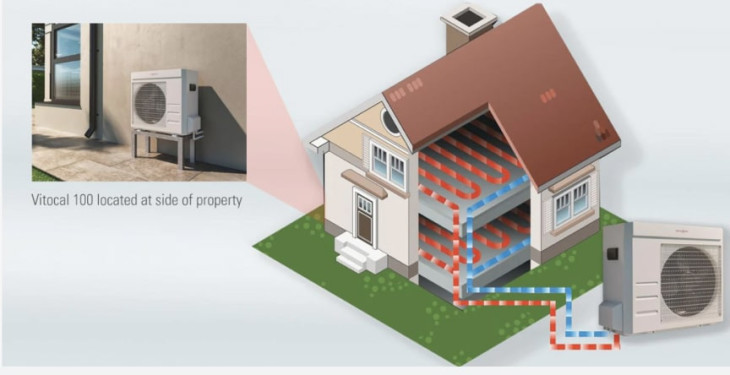
Ground source heat pumps (GSHPs) utilise the stable temperature of the ground or water sources to provide heating and cooling for your home. These systems are highly efficient, as the Earth's temperature remains relatively constant throughout the year.
GSHPs require an extensive network of pipes, either laid horizontally or drilled vertically, to extract heat. This can result in a higher initial installation cost. However, the long-term energy savings may outweigh this upfront investment.
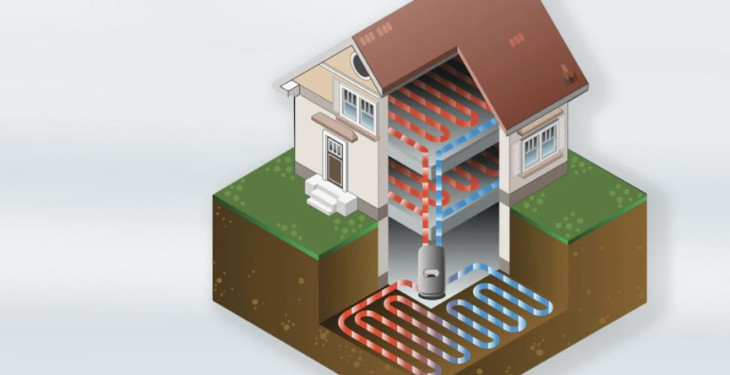
Geothermal heat pumps, also known as Earth-energy systems, use the Earth's core temperature to heat and cool homes. As the temperature below the surface remains stable, these heat pumps can work efficiently throughout the year.
Geothermal systems can be open-loop, which utilises groundwater, or closed-loop, where a fluid-filled pipe network is buried underground. Installation may require drilling deep boreholes, making it a costly and complex process, but the resulting energy efficiency and lowered environmental impact can be compelling.
Ductless mini-split systems are a type of ASHP that doesn't require the use of ductwork to deliver temperature-controlled air. They consist of an outdoor unit and one or more indoor units, making them ideal for homes with limited space or those without existing ducts.
Mini-split systems offer zoned heating and cooling, allowing you to adjust the temperature in individual rooms as needed. This flexibility, coupled with the ease of installation, can make ductless mini-splits a popular choice for energy-efficient home heating and cooling.
In summary, various heat pump technologies and installation types offer different benefits depending on your specific needs and home infrastructure. Each type provides heating and cooling in an energy-efficient manner, with the potential for significant energy savings compared to traditional gas boilers.
Heating and cooling systems play a pivotal role in maintaining a comfortable living environment.
The choice between a heat pump and a gas boiler often depends on various factors like efficiency, cost, and environmental impact. In recent years, heat pumps have gained popularity due to their energy efficiency and versatility in both heating and cooling applications.
Heat pumps work by transferring heat from one place to another, using a thermostat to regulate temperature. They are available in multiple types, such as air-source heat pumps and air-to-air systems. These systems can provide an all-in-one solution, functioning as heating, cooling, air filtration, and dehumidifier units.
Additionally, heat pumps can be used with different heating systems, including radiators and underfloor heating.
Gas boilers, on the other hand, generate heat by burning natural gas. They are commonly employed in central heating systems using radiators to distribute warmth throughout the house. The heat can also be transferred to a coil for hot water requirements.
Although gas boilers have been a traditional choice for many households, they can contribute to increased carbon emissions.
When it comes to efficiency, heat pumps are considered more energy-efficient, as they extract heat from the air, ground, or water, consuming less energy compared to gas boilers. Especially in regions with moderate climates (40-60 degrees), heat pumps can be an effective choice. However, their efficiency might decrease in colder regions.
Air-source heat pumps can be installed as ducted systems in homes, providing both heating and cooling options. This versatility reduces the need for separate air conditioning units, ultimately saving on energy costs. In contrast, gas boilers only serve the purpose of heating and typically require separate cooling systems.
Installing a heat pump can potentially lead to lower heating bills, especially if it is replacing an older, less efficient heating system. Nevertheless, be aware that some studies have found efficient gas boilers to be more cost-effective in certain situations.
In conclusion, the choice between heat pumps and gas boilers depends on several factors, such as the climate, house size, and energy-efficiency requirements. Carefully considering these elements will help homeowners determine the best option for their homes.
Heat pumps and gas boilers differ in their safety and noise aspects, playing a significant role in decision making for homeowners. When considering safety, it is vital to acknowledge the potential hazards associated with each system.
Gas boilers run on natural gas, which carries with it the risk of carbon monoxide poisoning. Carbon monoxide is a colourless, tasteless, and odourless gas that can be lethal in high concentrations.
To mitigate this, it is essential to install carbon monoxide detectors in the home and follow expert advice on regular maintenance. Heat pumps, on the other hand, operate without combustion, eliminating the threat of carbon monoxide poisoning.
In terms of noise, heat pumps are typically quieter than gas boilers. While both systems produce sound during operation, heat pumps often have lower noise levels, with newer models boasting near-silent operation.
Gas boilers may generate more noise, primarily when igniting and heating the system. Homeowners must take noise considerations into account, especially if the installation location is close to living spaces.
Efficiency matters in every heating system, but homeowners shouldn't overlook safety and noise considerations. Expert advice plays a significant role in choosing the optimal option for a specific environment.
Consulting with experts can help identify potential risks and provide guidance on installation and maintenance, ensuring a safe and comfortable home. So, while efficiency is essential, a balance between safety, noise, and efficiency aspects will result in an informed decision for the homeowner.
When considering heating options for your home, it is important to understand the common energy sources and their efficiency. There are several popular energy sources available for heating, including natural gas, electricity, oil, and propane.
Natural gas is a widely used fossil fuel for heating homes, and it powers gas boilers. It is obtained from underground reserves and transported through gas lines to residential properties. Natural gas is often preferred for its relatively low cost and high heating efficiency. However, it can release greenhouse gases when burned.
Electricity is another common energy source for heating, which is primarily generated from burning fossil fuels, nuclear power stations, and renewable sources like wind and solar.
Electric heat pumps and electric baseboard heaters utilise electricity to provide heating. Though the energy source is diverse, electric heating can be more expensive than natural gas, depending on your region and national grid rates.
Oil is another fossil fuel used to power oil boilers for home heating. Heating oil is derived from petroleum and may have a higher energy content than natural gas.
However, it is subject to fluctuations in oil prices, which can make it more expensive to use. Moreover, oil storage is necessary for homes using this heating method, creating additional costs and logistical concerns.
Propane is a byproduct of natural gas processing and petroleum refining. It is often used in rural areas where natural gas lines are not accessible.
Propane is stored in tanks and delivered to homes on a regular basis. While it is a versatile energy source, the cost of propane can also fluctuate with market conditions.
When comparing heat pumps and gas boilers, it is crucial to factor in the energy sources they use. Heat pumps typically rely on electricity, which might be renewable, and can be highly efficient when extracting heat from the surrounding air or ground.
On the other hand, gas boilers primarily use natural gas, a non-renewable fossil fuel. This difference can impact their respective efficiencies, as well as their environmental impact, so consider the energy source that best matches your needs, preferences, and long-term objectives.
When considering heat pumps and gas boilers, it's important to be aware of the various brands available in the market. Some prominent heat pump manufacturers include Daikin, Mitsubishi, and Fujitsu. On the other hand, top gas boiler brands include Worcester Bosch, Vaillant, and Baxi.
Installation and services play a critical role in the efficiency of heat pumps and gas boilers. It's essential to hire professional installers, such as those found through platforms like Angi, to ensure your HVAC system, both the outdoor and indoor units, are set up correctly for optimal performance.
Furthermore, regular maintenance is key for preserving your investment in a heating system.
This includes cleaning and checking both the outdoor unit, which contains the heat pump, and the indoor unit, housing the blower. Properly trained technicians can diagnose potential issues, perform necessary repairs, and extend the life of your system.
In addition to regular upkeep, be mindful of the following aspects for your heating system:
Filters: Regularly replace or clean filters to improve air quality and maintain the efficiency of your heat pump or gas boiler.
Insulation: Proper insulation helps to reduce heat loss, which keeps an even temperature in your home and lowers strain on your heating system.
Thermostats: Using programmable thermostats can help reduce energy consumption, saving money in the long run and reducing the environmental impact of your heating system.

To summarise, when evaluating heat pumps and gas boilers, being aware of brands, services and maintenance are vital factors. Engage reputable installers, carry out consistent maintenance, and educate yourself about best practices to ensure your heating system operates efficiently and effectively.

Furthermore, heat pumps can help reduce carbon emissions, making them an attractive, environmentally friendly choice. It is vital to evaluate factors such as installation costs, property requirements, and local climate when considering whether to switch from an oil boiler to a heat pump.
For more info on heat pump costs, check out our updated 2025 guide!
Last updated: 22nd September, 2025

Written by Stephen Day
Gas Safe Engineer at iHeat
Stephen Day is a Gas Safe registered and FGAS certified engineer with over 20 years of hands-on experience in the heating, cooling, and renewable energy industry, specialising in boiler installations, air conditioning, and heat pump systems.
LinkedInArticles by Stephen Day are reviewed by iHeat’s technical team to ensure accuracy and reliability.

27th February, 2026
Condensing boilers are considered to be some of the most efficient boilers out there on th...
 Read Article
Read Article

26th February, 2026
Vaillant boilers use a variety of parts to ensure efficient operation. This section looks...
 Read Article
Read Article

26th February, 2026
Leaving the heating on low all day might seem like a way to avoid the chill without bursti...
 Read Article
Read Article
No obligation. Takes less than 60 seconds.