

Written by Stephen Day
Gas Safe Engineer
Updated: 5th January, 2026
Explore the different types, costs, and efficiency of heat pumps in this blog post, illuminating their role as sustainable, cost-effective solutions for home heating and cooling.
Get a new boiler quote, save up to £550 per year (0% APR available).
Heat pumps have become an increasingly popular choice for homeowners seeking efficient and environmentally friendly heating and cooling solutions.
By functioning as a combined furnace and central air conditioner, heat pumps provide an all-in-one solution to keep your home comfortable all year round.
With various types available, including air-source, geothermal, and ductless mini-split systems, it is vital to make an informed decision based on your home's needs and your budget.
When considering heat pump costs, factors such as size, efficiency rating, brand, and type play a significant role. Installation costs can range from £2,000 to £20,000 or more, so it's essential to weigh the long-term energy savings and performance benefits against the initial investment.
(Modern gas boilers present an extremely cost-effective and efficient alternative to heat pumps)
Get a quote in 60 seconds, fitted as fast as next day!
0% APR finance available.
It's also worth exploring incentives, rebates, and other programs that can help make heat pump installation more affordable while enhancing the overall value of your home.
Heat pumps provide energy-efficient heating and cooling solutions for a variety of spaces. There are several common types of heat pumps, each with its own benefits and applications.
This section will cover air-source heat pumps, ground-source heat pumps, mini-split heat pumps, and geothermal heat pumps.
Air-source heat pumps absorb heat from the outdoor air and transfer it indoors for heating purposes. Conversely, during cooling mode, they extract heat from indoor air and release it outdoors. These pumps are popular due to their versatility and efficiency. Air-to-air systems, a subtype of air-source heat pumps, are especially common in mild climates and can be used for both residential and commercial spaces.
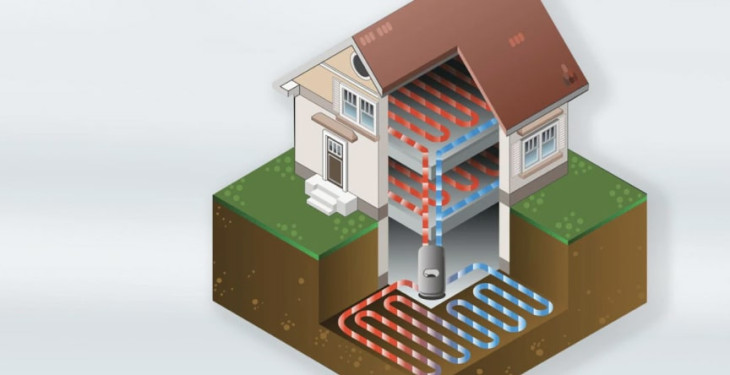
Ground-source heat pumps, also known as geothermal heat pumps, utilise the constant temperature of the earth to provide heating and cooling.
These systems involve underground pipes filled with fluid that absorb or disperse heat to or from the ground. While more expensive to install, ground-source heat pumps offer increased efficiency and can lead to long-term savings on energy bills.
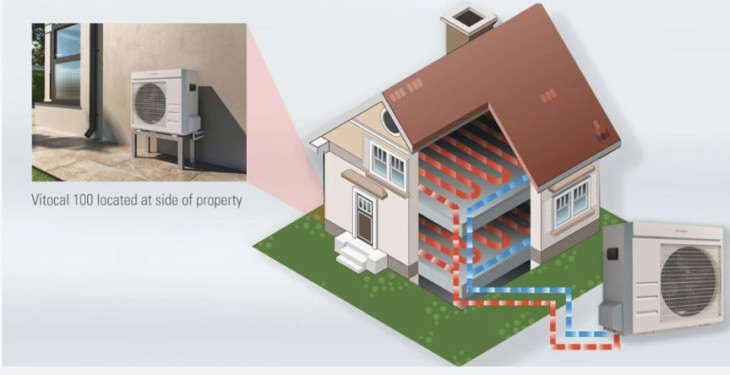
Mini-split heat pumps, also called ductless mini-split systems, are an effective solution for heating and cooling individual rooms or small spaces. Unlike central systems, mini-splits do not require ductwork, making them ideal for retrofit applications or newly constructed buildings.
Each mini-split unit provides temperature control for a specific area, offering increased flexibility and energy efficiency.
Geothermal heat pumps are a type of ground-source heat pump that takes advantage of the earth's stable temperature below the surface.
They function by circulating a fluid through a closed-loop system of pipes buried in the ground. As the fluid absorbs heat from the earth, it transfers it to the indoor spaces for heating, while the reverse process occurs for cooling.
While the installation costs of geothermal heat pumps can be considerable, their high efficiency and lower operating costs make them an attractive long-term investment.
The type of heat pump system you choose significantly impacts costs. Here are the most common types:
Air-to-Air Heat Pumps: Transfers heat between indoor and outdoor air, typically costing less than other types.
Ground-Source (Geothermal) Heat Pumps: Extracts heat from the earth, offering higher efficiency but also higher installation costs.
Ductless Mini-Split Systems: Suitable for homes without existing ductwork, as they use individual units to heat and cool specific rooms.
The system type affects not only the upfront investment but also the overall efficiency and suitability for your home.
Larger homes require higher-capacity heat pumps, which increase costs. Existing ductwork can also impact expenses; if your ductwork needs repair or replacement, this will add to the total cost. Homes without ducts may benefit from ductless systems, which avoid ductwork modifications.
Your installation location and climate will influence the complexity and cost of installation. Areas with extreme temperatures may require higher-performance heat pumps, which are generally more expensive. Hard-to-reach locations can also raise installation costs.
Higher efficiency models, often with superior Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) and Heating Seasonal Performance Factor (HSPF) ratings, come with a premium price. However, these models often lead to long-term savings by reducing energy consumption.
Brand reputation and product quality matter. Trusted brands typically offer robust warranties and produce durable products, which can be more expensive but reduce long-term maintenance costs.
Heat pump prices vary based on type and brand. Here’s a general cost range for different systems:
Air-Source Heat Pumps: £3,000 to £6,000
Ground-Source Heat Pumps: £11,000 to £26,000
Ductless Mini-Splits: £1,100 to £2,600 per zone
The system size, type, and efficiency rating impact overall equipment costs, so select a system that matches your budget and home needs.
Installation labour costs typically range between £2,000 and £6,000, depending on the complexity. Simpler air-source and mini-split systems tend to cost less to install, whereas geothermal installations or projects requiring ductwork changes are often pricier.
Additional components may be required for certain installations:
Thermostats: £50 - £300
Ductwork Repairs: £10 - £30 per linear foot
Ground Loop Installation (Geothermal): £6,000 and above
Understanding all parts and materials helps you get a complete picture of total costs.
Various UK government schemes can offset heat pump installation costs, making these systems more accessible:
Boiler Upgrade Scheme (BUS): Offers up to £7,500 for air-source and ground-source heat pumps, and £5,000 for biomass boilers.
Great British Insulation Scheme: Assists with home insulation improvements, which can lower energy bills.
Energy Company Obligation (ECO): Requires energy suppliers to help households install energy-saving measures, such as heating system upgrades or insulation.
Check eligibility requirements and application processes for these schemes to maximise available financial support.
Heat pumps are highly efficient as they transfer heat rather than generate it. They can save up to 20-30% on energy costs compared to standard heating systems, making them a great choice for energy-conscious homeowners. However, the savings you can achieve will depend on the system being replaced, as well as current electricity costs.
To maximise savings, look for ENERGY STAR-certified models with high SEER and HSPF ratings, which guarantee optimal efficiency.
Keep in mind that insulation, proper installation, and appropriate sizing also play critical roles in a heat pump’s effectiveness and efficiency. In mild climates, heat pumps provide significant savings, while in colder areas, models designed for low temperatures offer the best performance.
Regular maintenance is essential for extending a heat pump’s lifespan, which generally ranges from 10 to 25 years. Routine tasks, such as cleaning or replacing filters and clearing debris, can be done by homeowners, while complex tasks require a professional. Maintenance costs typically range from £150 to £1,950, depending on service complexity. Investing in preventative maintenance is highly recommended as it can reduce energy costs by up to 25%.
When evaluating heat pump costs, other factors like insulation, existing ductwork, and windows play a role in overall system efficiency:
Insulation: Proper insulation reduces heat loss, lowering operational costs.
Solar Integration: Combining solar power with your heat pump system can reduce electricity costs.
Windows: Energy-efficient windows help stabilise indoor temperatures, minimising heat pump usage.
Duct Compatibility: Properly sealed and insulated ducts improve airflow, boosting system efficiency.
For some households, a modern gas boiler may be a more practical choice, offering an efficient, cost-effective heating solution. iHeat offers free fixed-price quotes within 60 seconds, helping you find the right boiler for your home’s heating needs.
Popular Boiler Installation Types and Costs:
Combi to Combi Swap: £1,845
System to Combi Conversion: £2,499
New Boiler Installation: £2,899
Back Boiler to Combi: £3,299
Last updated: 5th January, 2026

Written by Stephen Day
Gas Safe Engineer at iHeat
Stephen Day is a Gas Safe registered and FGAS certified engineer with over 20 years of hands-on experience in the heating, cooling, and renewable energy industry, specialising in boiler installations, air conditioning, and heat pump systems.
LinkedInArticles by Stephen Day are reviewed by iHeat’s technical team to ensure accuracy and reliability.

27th February, 2026
Condensing boilers are considered to be some of the most efficient boilers out there on th...
 Read Article
Read Article

26th February, 2026
Vaillant boilers use a variety of parts to ensure efficient operation. This section looks...
 Read Article
Read Article

26th February, 2026
Leaving the heating on low all day might seem like a way to avoid the chill without bursti...
 Read Article
Read Article
No obligation. Takes less than 60 seconds.