

Written by Stephen Day
Gas Safe Engineer
Updated: 15th August, 2025
In this UK heat pump vs new gas boiler comparison guide, we'll be taking a look at which type of system is the best for savings!
Get a new boiler quote, save up to £550 per year (0% APR available).
In recent years, the debate between heat pumps and boilers has gained traction as homeowners look for efficient and cost-effective ways to heat their homes.
A key component of this discussion revolves around the question of whether a heat pump is a cheaper option to run than a boiler. To answer this question, it is essential to examine the efficiencies of both systems, as well as their operating costs and environmental impact.
Heat pumps operate by extracting heat from the outside air and transferring it inside the home for heating purposes, offering impressive efficiency levels of 300-400%. In contrast, boilers typically rely on natural gas or oil to generate heat, which may not be as efficient or environmentally friendly.
As gas prices have risen, heat pump running costs have become increasingly competitive.
Meanwhile, boilers have long been considered the go-to option for home heating, particularly because they are often a cheaper boiler installation option.
Get a quote in 60 seconds, fitted as fast as next day!
0% APR finance available.
However, the increasing popularity of heat pumps has prompted a shift in the heating industry, with many consumers now looking to make the switch due to the potential energy savings and reduced environmental impact.
Find out more about heat pumps in our 2025 new boiler cost guide!
Heat pumps and boilers are two popular heating systems for homes, with each offering unique advantages and limitations. In this section, we examine various types of heat pumps and boilers, highlighting their key features and factors that influence their performance.
Heat pumps are renewable energy systems that extract heat from a source such as the air, ground, or water and transfer it to heat your home and hot water.
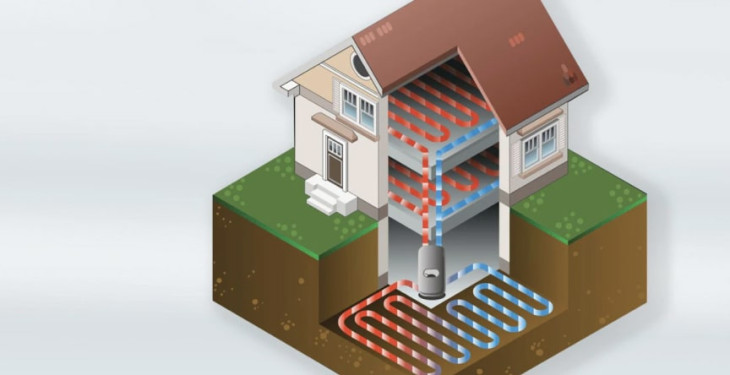
There are two main types of heat pumps: air source heat pumps and ground source heat pumps. They use electricity to power their operation, and this can come from renewable sources, making them a more environmentally friendly option.
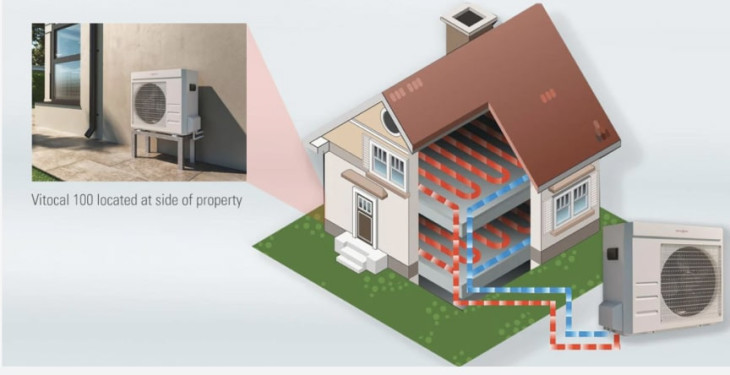
On the other hand, boilers are a more traditional heating system that burn fuel to heat water, which is then circulated through radiators or underfloor heating pipes to warm your home.
Boilers can be powered by a variety of fuels, including natural gas, oil, electricity, and biomass. The common types of boilers include the following:
Gas boiler: Burns natural gas to heat water. They are the most common type of boiler.
Oil boiler: Uses oil as fuel to heat water, typically found in rural areas with limited access to natural gas.
Electric boiler: Heats water using electricity, making them an option for homes without gas supply.
Biomass boiler: Burns wood pellets or logs to heat water, offering a renewable and low-carbon alternative to fossil fuel boilers.
Boiler systems are further classified into combi, system, and regular boilers:
Combi boiler: A combination boiler provides both heating and hot water directly from the mains, eliminating the need for a separate hot water cylinder.
System boiler: Works with a hot water cylinder, which stores hot water, but doesn't require a cold water tank.
Regular boiler: Also known as a traditional or conventional boiler, it requires both a hot water cylinder and a cold water tank for their operation.
Choosing the right heating system – a heat pump or a boiler – requires considering factors such as energy efficiency, running costs, installation costs, maintenance, and environmental impact.
While heat pumps are generally more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly, they can be costlier to install and may have higher electricity costs compared to gas boilers. The choice ultimately depends on individual preferences, home size, location, and access to energy sources.
Heat pumps are known to be energy-efficient heating appliances compared to traditional boilers. Their energy efficiency comes from their ability to extract and utilise heat from the environment, such as air, ground or water. This results in less energy being consumed to generate heat for your home. For instance, a furnace or boiler that burns fossil fuel (natural gas, propane, or heating oil) has an efficiency that ranges from about 78% to 98%, while a heat pump, fuelled by electricity, can reach even an efficiency of 100%.
In the context of energy-efficient gas boilers, it is worth mentioning that they have advanced features to reduce energy consumption and release fewer emissions.
However, heat pumps still have an edge in overall efficiency, especially when combined with systems like underfloor heating or large, specially designed oversized radiators.
Coefficient of Performance (COP) is a pivotal factor when comparing heat pump efficiency with that of boilers.
A higher COP value indicates a more efficient heating appliance. With a COP of about 3, a heat pump starts to become cheaper to run than a gas boiler, which typically operates at an efficiency of about 85%. In the past, a COP of around 3.7 was necessary to achieve the same running costs as a gas boiler.
Taking into account the efficiency, energy usage, and COP, an air-source heat pump can be a more cost-effective and environmentally friendly option for heating your home, compared to gas or oil boilers.
Additionally, if the proper insulation measures are in place, the performance and effectiveness of a heat pump can be maximised, further increasing the potential savings and reduction in carbon emissions.
In conclusion, the efficiency and performance of heat pumps make them a preferred choice for many homeowners seeking cost savings and a lower carbon footprint.
This section compares the operating costs of heat pumps and boilers, focusing on heating costs, running costs, and annual energy bills. The goal is to provide readers with reliable information to make an informed decision regarding which system may be more cost-effective.

Heat pump costs and gas boilers costs are different due to the energy sources they rely on. Heat pumps use electricity to extract heat from the outside air and transfer it into the home, while gas boilers generate heat by burning natural gas.
Heat pumps boast an impressive efficiency range of 300% to 500%, as they can provide up to three to five times the amount of heat energy they consume. Conversely, gas boilers typically have an efficiency rate of around 90%, meaning that for every kWh of gas consumed, they produce around 90% of heat energy. This variation in efficiency has a significant impact on heating costs.
Find out more about heat pumps in our 2025 cost guide!
When comparing running costs, it's essential to consider the cost per kWh of the fuel used. In general, electricity tends to be more expensive than natural gas.
In fact, electricity can be as much as three times the cost of gas as a central heating system fuel!
However, due to the high efficiency of heat pumps, they can still be cost-effective despite the higher electricity costs.
The choice of a heat pump or gas boiler can significantly impact an average household's annual energy bills.
However, it is essential to factor in the specific geographical location and energy tariffs, as these can influence the cost-effectiveness of heat pumps and gas boilers.
When comparing heat pump vs gas boiler costs, it's important to weigh the benefits of each system and consider factors such as efficiency, fuel costs, and environmental impact. Although heat pumps may have higher upfront costs, they can provide long-term savings through lower energy bills and reduced reliance on fossil fuels like natural gas, heating oil, or propane.
Heat pumps and boilers have different environmental impacts, especially in terms of carbon emissions.
Boilers, which primarily use fossil fuels like natural gas, release significant amounts of carbon dioxide – a major contributor to climate change. On the other hand, heat pumps operate using electricity, and their carbon emissions depend on the source of the electricity.
A very efficient heat pump can result in huge savings on heating bills compared to a gas boiler, contributing to a lower carbon footprint.
However, if the electricity comes from fossil fuel-based power plants, the environmental benefits may be limited.
Heat pumps can be integrated with various renewable energy technologies, making them even more environmentally friendly.
For example, geothermal heat pumps utilise the constant temperature beneath the earth's surface to heat and cool buildings. They are more efficient and emit fewer carbon emissions than conventional electric heat pumps and gas boilers.
Proper insulation is crucial for the optimal performance of both heat pumps and boilers. Homeowners must ensure that their homes are well-insulated to prevent heat loss and achieve maximum energy efficiency.
Insulation in walls, floors, roofs, and windows should be prioritised to reduce the overall heating load on the system. This reduces the operational costs and increases the overall effectiveness of both heat pumps and boilers.
Radiators and underfloor heating systems contribute significantly to a home's insulation requirements. Underfloor heating, in particular, is compatible with heat pumps, as it requires lower water temperatures.
On the other hand, homeowners may need to upgrade their radiators to work efficiently with heat pumps due to the lower water temperature output.
Heat Pumps: The main components of a heat pump include a compressor, a condenser, an evaporator, expansion devices, and a thermostat. In an air-to-air heat pump, the system extracts heat from the outdoor air and transfers it indoors.
In contrast, a ductless mini-split heat pump is convenient for homes that do not have existing ductwork, focusing on heating specific rooms or areas.
Heat pump installation typically involves setting up the outdoor unit (compressor and condenser) and the indoor unit (air handler), connecting the pipes, and laying down cables. It may also be necessary to install additional elements, such as vents or ductwork in certain situations.
The maintenance of a heat pump system generally involves regular filter cleaning and periodic inspection of the compressor and other components.
Boilers: Boilers heat water that circulates through pipes and radiators or underfloor heating systems to warm the home. The main components of a boiler system include the boiler itself, a feed tank, an expansion tank, a hot water storage cylinder, and a thermostat.
A boiler system may be combined with an HVAC system, but it typically operates independently to provide central heating and hot water production.
Installation and maintenance of boilers can be more complex than heat pumps, as they involve gas or oil-related connections, venting, and pipework.
Boilers may also need chemical treatments to prevent corrosion and mineral buildup that can reduce their efficiency. Regular servicing, which includes checking the burner, heat exchanger, and fuel supply components, is essential for safe and efficient boiler operation.
When considering the comfort and convenience of heat pumps and boilers, there are several factors to consider. Both systems have their own pros and cons, and choosing between them involves weighing their respective benefits and drawbacks.
Expert advice can help guide you towards the best option for your specific needs and local weather conditions.
Heat pumps are highly versatile and efficient in both cooling and heating a home. They operate by extracting heat from the outside air, even in cold conditions, and transferring it indoors. This highly efficient process makes them a popular choice for those looking for eco-friendly HVAC systems.
Heat pumps can maintain a consistent temperature indoors, providing a comfortable environment year-round. In areas with mild winters, a heat pump may be an excellent option for providing consistent heating without the need for traditional furnace- or boiler-based systems.
On the other hand, boilers are well-known for their ability to provide a high level of warmth and comfort in colder climates. Boilers produce heat by burning natural gas or oil, and then distribute this heat throughout the home via radiators, underfloor heating or hot water systems.
This highly effective method consistently provides a pleasant indoor environment, effectively combating the chill of colder months. Boilers can also offer a certain level of reliability, as they often have a longer service life when compared to some heat pump systems.
However, boilers do rely on non-renewable fuels, which may not be the best choice for those wanting to adopt a more sustainable approach to heating and cooling.
Furthermore, the distribution of heat through radiators may not be as evenly spread as the heat provided by a heat pump, resulting in potential hot and cold spots in a home.
Ultimately, the most suitable choice between heat pumps and boilers depends on factors such as the climate, the size and layout of the home, and personal preferences for comfort and convenience.
Consulting with an HVAC expert can provide valuable insights into which system would be the best fit for your individual requirements.
The UK government has introduced several schemes and incentives to encourage the adoption of heat pumps as a more efficient and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional boilers.
The Boiler Upgrade Scheme (BUS) offers significant financial assistance to help homeowners and small businesses transition from traditional boilers to more energy-efficient heating solutions. Key details of the scheme include:
Air Source Heat Pumps: Grants of £7,500.
Ground Source Heat Pumps: Grants of £7,500.
Biomass Boilers: Grants of £5,000.
This scheme aims to make heat pumps more accessible by covering a substantial portion of the installation costs. The scheme is set to run from 2022 to 2025 with £450 million in funding, and has been extended to April 2028 with an additional £1.5 billion in funding.
Homeowners can benefit from a 30% tax credit of up to £5,000 on new heat pump installations. This tax credit reduces the upfront costs significantly, making heat pumps a more attractive option compared to traditional boilers.
There are various rebates available to further support the installation of heat pumps:
Low-Income Households: Access to significant rebates, making energy-efficient heating solutions affordable.
Middle-Income Households: Potential savings of around £2,896 on the installation of a heat pump due to these rebates.Alternatives and Future Developments
Gas furnace technology has come a long way and continues to develop, offering a viable alternative to heat pumps. With high-performance systems, a gas furnace can achieve greater energy efficiency and reduce carbon emissions.
Rather than relying solely on fossil fuels, natural gas furnaces, for example, utilise more environmental-friendly alternatives such as biogas.
Furthermore, advances in gas furnace technology have led to improved kilowatt hour (kWh) usage, resulting in lower running costs for homeowners. Well-insulated homes can benefit greatly from these improvements while also reducing overall environmental impact.
High-performance HVAC systems, which include both heating and air conditioning, offer another possible solution for energy-efficient home temperature control.
These advanced systems utilise cutting-edge technology to optimise energy usage and improve overall efficiency. Some noteworthy features of high-performance HVAC systems include:
Smart controls: These allow homeowners to adjust settings remotely, providing increased flexibility and enhancing energy management.
Variable speed capabilities: High-performance systems can operate at lower speeds for longer periods, leading to consistent temperatures and increased energy savings.
Zoning: Dividing your home into separate "zones" enables the HVAC system to cool or heat specific areas more effectively, reducing energy waste.
Adopting high-performance HVAC systems can significantly reduce energy consumption and costs when compared to traditional boilers or heat pumps.
As technology continues to evolve, these systems are expected to become increasingly prevalent, offering a cost-effective and environmentally conscious option for homeowners.
Overall, the choice between a heat pump system, a boiler, or other alternatives depends on individual preferences and circumstances.
Homeowners should weigh the energy efficiency, environmental impact, and long-term costs of each option to make the best decision for their energy needs.

In conclusion, the cost comparison between heat pumps and boilers will vary depending on individual circumstances and preferences. Each system has its unique set of advantages, and careful research and consideration are required to make the most informed decision.
Last updated: 15th August, 2025

Written by Stephen Day
Gas Safe Engineer at iHeat
Stephen Day is a Gas Safe registered and FGAS certified engineer with over 20 years of hands-on experience in the heating, cooling, and renewable energy industry, specialising in boiler installations, air conditioning, and heat pump systems.
LinkedInArticles by Stephen Day are reviewed by iHeat’s technical team to ensure accuracy and reliability.

27th February, 2026
Condensing boilers are considered to be some of the most efficient boilers out there on th...
 Read Article
Read Article

26th February, 2026
Vaillant boilers use a variety of parts to ensure efficient operation. This section looks...
 Read Article
Read Article

26th February, 2026
Leaving the heating on low all day might seem like a way to avoid the chill without bursti...
 Read Article
Read Article
No obligation. Takes less than 60 seconds.